In this guide I will illustrate how to set up the code for a protocol for our microagent to query the state of a table at a restaurant and possibly book it if available. First of all, create a script and name it booking_protocol.py.
touch booking_protocol.py
Let's then create our two agents: customer and restaurant. These 2 agents interact in the following way:
We are now ready to write the code for our example. We need to consider each step above separately, but first, we need to define the different classes for messages to be exchanged between the customer and restaurant agents.
from enum import Enum from uagents import Agent, Bureau, Context, Model class TableStatus(str, Enum): RESERVED = "reserved" FREE = "free" class QueryTableRequest(Model): table_number: int class QueryTableResponse(Model): status: TableStatus class BookTableRequest(Model): table_number: int class BookTableResponse(Model): success: bool
We import the enum class from the Enum module. Enum is a class in python for creating enumerations, which are a set of symbolic names bound to unique, constant values.
We then import the custom classes Agent, Bureau, Context, Model from the uagents library.
We then proceed by defining the following classes for messages to be exchanged between our Microagents:
TableStatus: this is an enumeration that defines two possible values: RESERVED and FREE for the table at the restaurant.
QueryTableRequest: It has one attribute, table_number, which is an integer. This class is used to define a message that can be sent from a customer agent to a restaurant agent to query the availability of a table.
QueryTableResponse: It has one attribute, status, which is of type TableStatus. This class is used to define a message that can be sent from a restaurant agent to a customer agent to confirm the availability of a table.
BookTableRequest: It has one attribute, table_number, which is an integer. This class is used to define a message that can be sent from a customer agent to a restaurant agent to request to book a table.
BookTableResponse: It has one attribute, success, which is a boolean. This class is used to define a message that can be sent from a restaurant agent to a customer agent to confirm whether the table booking was successful or not.
Now, we are ready to create our two Microagent instances of the class Agent: Customer and Restaurant.
customer = Agent(name = "Customer") restaurant = Agent(name = "Restaurant")
We then proceed by defining each agent's behavior and functions to be executed. We first consider the customer agent then the restaurant agent.
@customer.on_interval(period=3.0, messages=QueryTableRequest) async def interval(ctx: Context): started = ctx.storage.get("started") if not started: await ctx.send(restaurant.address, QueryTableRequest(table_number=42)) ctx.storage.set("started", True)
The purpose of this decorator is to have the user agent sending a query message to the restaurant agent every 3 seconds to query for the availability of table number 42. The started key is used to ensure that the query message is only sent once when the agent starts running.
@customer.on_message(QueryTableResponse, replies=BookTableRequest) async def handle_query_response(ctx: Context, _sender: str, msg: QueryTableResponse): if msg.status == TableStatus.FREE: ctx.logger.info("Table is free, attempting to book it now") await ctx.send(restaurant.address, BookTableRequest(table_number=42)) else: ctx.logger.info("Table is not free - nothing more to do")
@customer.on_message(BookTableResponse, replies=set()) async def handle_book_response(ctx: Context, _sender: str, msg: BookTableResponse): if msg.success: ctx.logger.info("Table reservation was successful") else: ctx.logger.info("Table reservation was UNSUCCESSFUL")
@restaurant.on_message(model=QueryTableRequest, replies=QueryTableResponse) async def handle_query_request(ctx: Context, sender: str, msg: QueryTableRequest): if ctx.storage.has(str(msg.table_number)): status = TableStatus.RESERVED else: status = TableStatus.FREE ctx.logger.info(f"Table {msg.table_number} query. Status: {status}") await ctx.send(sender, QueryTableResponse(status=status))
@restaurant.on_message(model=BookTableRequest, replies=BookTableResponse) async def handle_book_request(ctx: Context, sender: str, msg: BookTableRequest): if ctx.storage.has(str(msg.table_number)): success = False else: success = True ctx.storage.set(str(msg.table_number), sender) await ctx.send(sender, BookTableResponse(success=success))
We have defined both of our agents and their respective behaviors and functions. Since we have multiple agents in this example we add them to a bureau, so for them to be run at the same time.
bureau = Bureau() bureau.add(user) bureau.add(restaurant) if __name__ == "__main__": bureau.run()
The overall code for this example should look as follows:
from enum import Enum from uagents import Agent, Bureau, Context, Model class TableStatus(str, Enum): RESERVED = "reserved" FREE = "free" class QueryTableRequest(Model): table_number: int class QueryTableResponse(Model): status: TableStatus class BookTableRequest(Model): table_number: int class BookTableResponse(Model): success: bool user = Agent(name="user") restaurant = Agent(name="restaurant") @customer.on_interval(period=3.0, messages=QueryTableRequest) async def interval(ctx: Context): started = ctx.storage.get("started") if not started: await ctx.send(restaurant.address, QueryTableRequest(table_number=42)) ctx.storage.set("started", True) @customer.on_message(QueryTableResponse, replies=BookTableRequest) async def handle_query_response(ctx: Context, _sender: str, msg: QueryTableResponse): if msg.status == TableStatus.FREE: ctx.logger.info("Table is free, attempting to book it now") await ctx.send(restaurant.address, BookTableRequest(table_number=42)) else: ctx.logger.info("Table is not free - nothing more to do") @customer.on_message(BookTableResponse, replies=set()) async def handle_book_response(ctx: Context, _sender: str, msg: BookTableResponse): if msg.success: ctx.logger.info("Table reservation was successful") else: ctx.logger.info("Table reservation was UNSUCCESSFUL") @restaurant.on_message(model=QueryTableRequest, replies=QueryTableResponse) async def handle_query_request(ctx: Context, sender: str, msg: QueryTableRequest): if ctx.storage.has(str(msg.table_number)): status = TableStatus.RESERVED else: status = TableStatus.FREE ctx.logger.info(f"Table {msg.table_number} query. Status: {status}") await ctx.send(sender, QueryTableResponse(status=status)) @restaurant.on_message(model=BookTableRequest, replies=BookTableResponse) async def handle_book_request(ctx: Context, sender: str, msg: BookTableRequest): if ctx.storage.has(str(msg.table_number)): success = False else: success = True ctx.storage.set(str(msg.table_number), sender) await ctx.send(sender, BookTableResponse(success=success)) bureau = Bureau() bureau.add(customer) bureau.add(restaurant)
To run the script, go on your terminal, make sure you are in the right directory for your Microagent project and that you activated your virtual environment. Run the script:
python booking_protocol.py
You should get the following output:
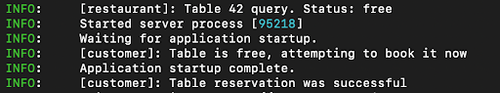
We successfully created two Microagents, Customer and Restaurant, with the customer agent querying for availability of table 42 at the restaurant and possibly book it. The restaurant agent, in turn, checks for availability of the table and answers back with the status of such booking request. In our case, booking is successful.